1. Cardiovascular
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Enlarged Heart
- Cor Pulmonale
- Varicose Veins
- Pulmonary Embolism

a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to the body’s other organs.

an increase in the size of the heart that may be caused by a thickening of the heart muscle because of increased workload.
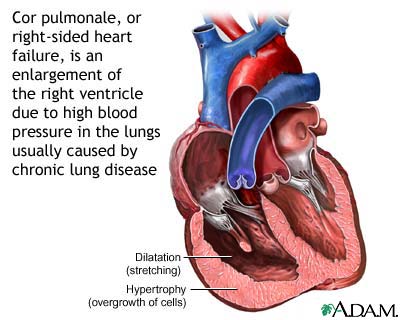
Also known as right heart failure. Cor pulmonale is a change in structure and function of the right ventricle of the heart as a result of a respiratory disorder.
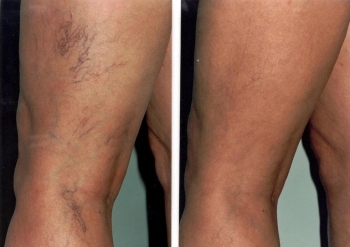
Twisted, enlarged veins that mostly affects the lower body as a result of pressuring the veins.

Blockage of the pulmonary artery (or one of its branches) by a blood clot, fat, air, amniotic fluid, injected talc or clumped tumor cells that results in difficulty breathing, pain during breathing, and more rarely circulatory instability and may result in death.
2. Endocrine
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
- Menstrual Disorder
- Infertility

Cysts (fluid-filled sacs) in the ovaries that result in high levels of androgens (male hormones) and missed or irregular periods.
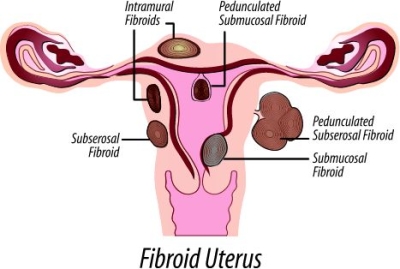
is a physical or emotional problem that interferes with the normal menstrual cycle, causing pain, unusually heavy or light bleeding, delayed menarche, or missed periods.

inability for a man or woman to contribute to conception.
3. Gastrointestinal
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Fatty Liver Disease
- Cholelithiasis (gallstones)
- Hernia
- Colorectal Cancer

happens when the LES ,a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus that acts like a valve between the esophagus and stomach, opens spontaneously for varying periods of time which causes stomach contents along with digestive juices to rise up into the esophagus (the tube that carries food from mouth to stomach).

an accumulation of fat within the liver that may cause liver-damaging inflammation and, sometimes, the formation of fibrous tissue. In some cases, this can progress either to cirrhosis, which can produce progressive, irreversible liver scarring, or to liver cancer.

Gallstones form when bile, liquid that help the body digest fats, that is stored in the gallbladder hardens into pieces of stone-like material. Happens when bile contains too much cholesterol.

occurs when the contents of a body cavity bulge out of the area where they are normally contained. These contents, usually portions of intestine or abdominal fatty tissue, are often enclosed in the thin membrane that naturally lines the inside of the cavity.

also known as colon cancer, is cancerous growths in the colon, rectum and appendix. It is the third most common form of cancer and the second leading cause of death among cancers in the Western world.
4. Renal and Genitourinary
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Urinary Incontinence
- Chronic Renal Failure
- Hypogonadism
- Breast Cancer
- Uterine Cancer
- Unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Trouble urinating
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Stillbirth
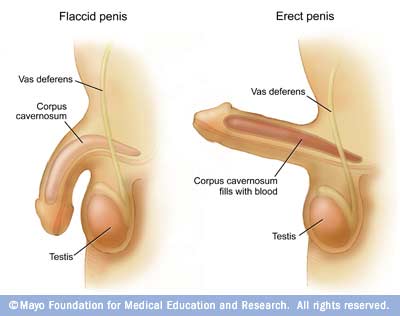
also known as impotence is the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.

is the loss of bladder control that results in mild leaking to uncontrollable wetting

is a gradual and progressive loss of the ability of the kidneys to excrete wastes, concentrate urine, and conserve electrolytes.

happens when the sex glands produce little or no hormones. In men, these glands (gonads) are the testes; in women, they are the ovaries.
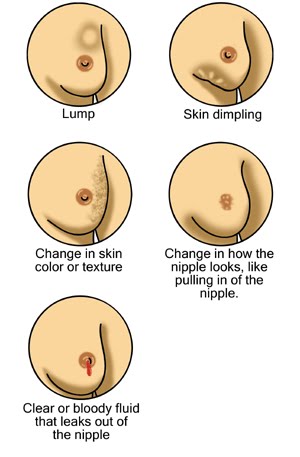
is the most common cancer among women.

Symptoms include

occurs when a fetus which has died in the womb or during labour or delivery exits its mother’s body.
5. Integument (skin and appendages)
- Stretch Marks
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- Lymphedema
- Cellulitis
- Carbuncles
- Intertrigo

are fine lines that appear on the skin that appears when a person grows or gains weight really fast.

velvety, light-brown-to-black, markings usually on the neck, under the arms or in the groin.

is a condition of localized fluid retention caused by a compromised lymphatic system. Danger lies in the constant risk of developing an uncontrolled infection in the affected limb.

Cellulitis appears as a swollen, red area of skin that feels hot and tender, and it may spread rapidly.

a skin infection that often involves a group of hair follicles. The infected material forms a lump, called mass, which occurs deep in the skin.

bacterial, fungal, or viral infection that has developed at the site of broken skin due to inflammation.
6. Musculoskeletal
- Hyperuricemia
- Immobility
- Osteoarthritis
- Low Back Pain
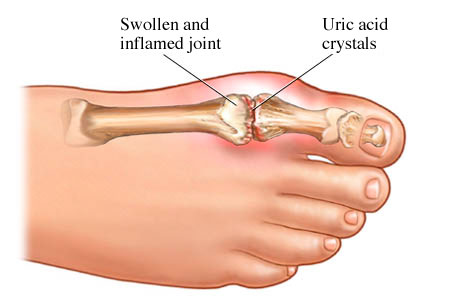
High level of uric acid in the blood that will most likely lead to gout.

is the disease that requires complete bed rest or extremely limits your activity.

is a joint disease caused by the breakdown and loss of the cartilage of one or more joints.
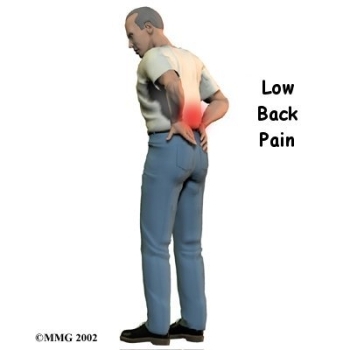
is the result of trauma to the lower back or a disorder such as arthritis.
7. Neurologic
- Stroke
- Meralgia Paresthetica
- Headache
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Dementia
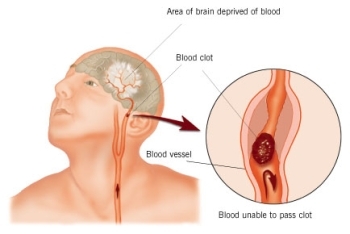
is a rapidly developing loss of brain function due to an interruption in the blood supply to all or part of the brain.

is a disorder characterized by tingling, numbness, and burning pain in the outer side of the thigh.

is a condition of pain in the head.

occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist. The median nerve controls sensations to the palm side of the thumb and fingers, as well as impulses to some small muscles in the hand that allow the fingers and thumb to move.

is the progressive decline in cognitive function due to damage or disease in the brain beyond what might be expected from normal aging.
8. Respiratory
- Dyspnea
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Hypoventilation Syndrome
- Pickwickian Syndrome
- Asthma

also known as short of breath (SOB) is perceived difficulty breathing or pain on breathing.
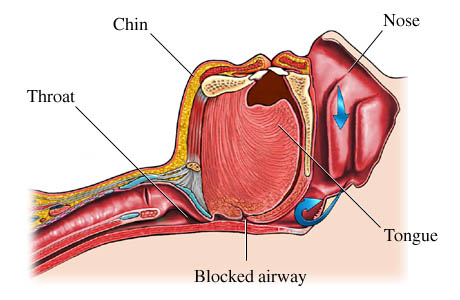
is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep with each breathless period lasting long enough so one or more breaths are missed, and occur repeatedly throughout sleep.
occurs when a very obese person does not breathe enough oxygen while sleeping. Comes from a defect in the brain’s control over breathing and excessive weight (due to obesity) against the chest wall, which makes it hard for a person to take a deep breath. As a result, the blood has too much carbon dioxide and not enough oxygen.

is the combination of severe obesity, suffering from obstructive sleep apnea causing hypoxia and hypercapnia resulting in marked daytime somnolence and chronic respiratory acidosis.

is a chronic disease that affects your airways, which are the tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs.
9. Psychological
- Depression
- Low Self Esteem
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Social Stigmatization

is a state of intense sadness, melancholia or despair that has advanced to the point of being disruptive to an individual’s social functioning and/or activities of daily living.

is a low overall of a person’s self-appraisal of their worth.

is a mental disorder that involves a disturbed body image.

is severe social disapproval of personal characteristics or beliefs that are against cultural norms.
No comments:
Post a Comment